How the Triangular Rotor Revolutionized Engine Design
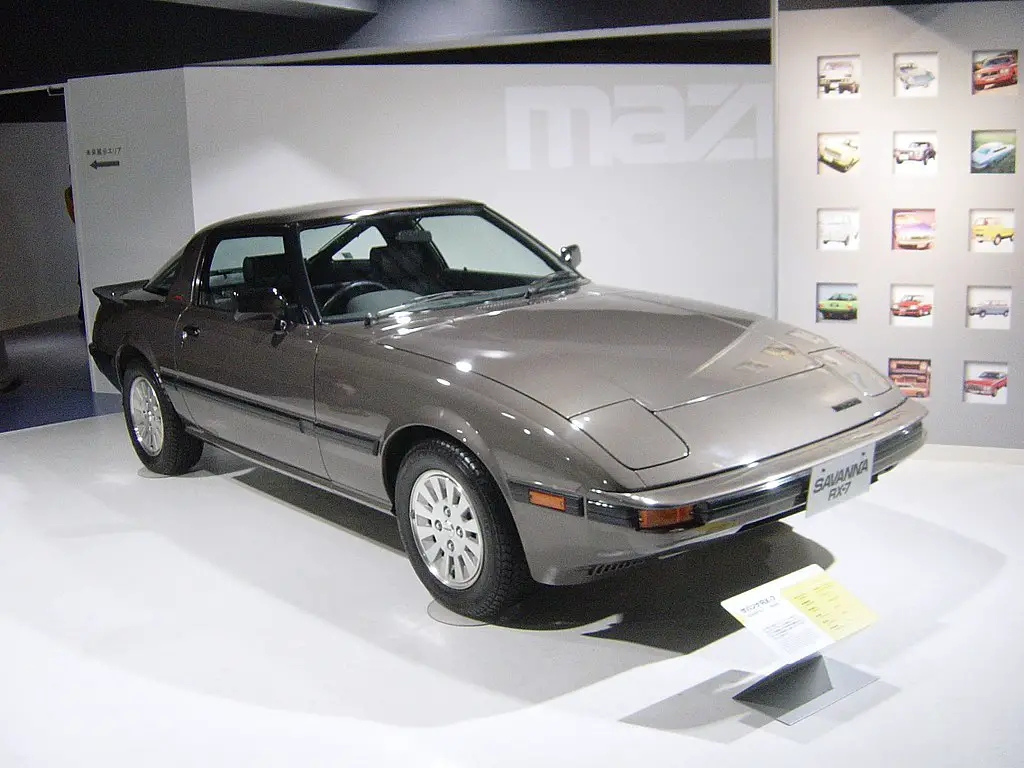
The Mazda RX7, with its unique rotary engine, holds a special place in automotive history. From its debut in 1978 to its discontinuation in 2002, this sports car captivated enthusiasts with its innovative design and exceptional performance.
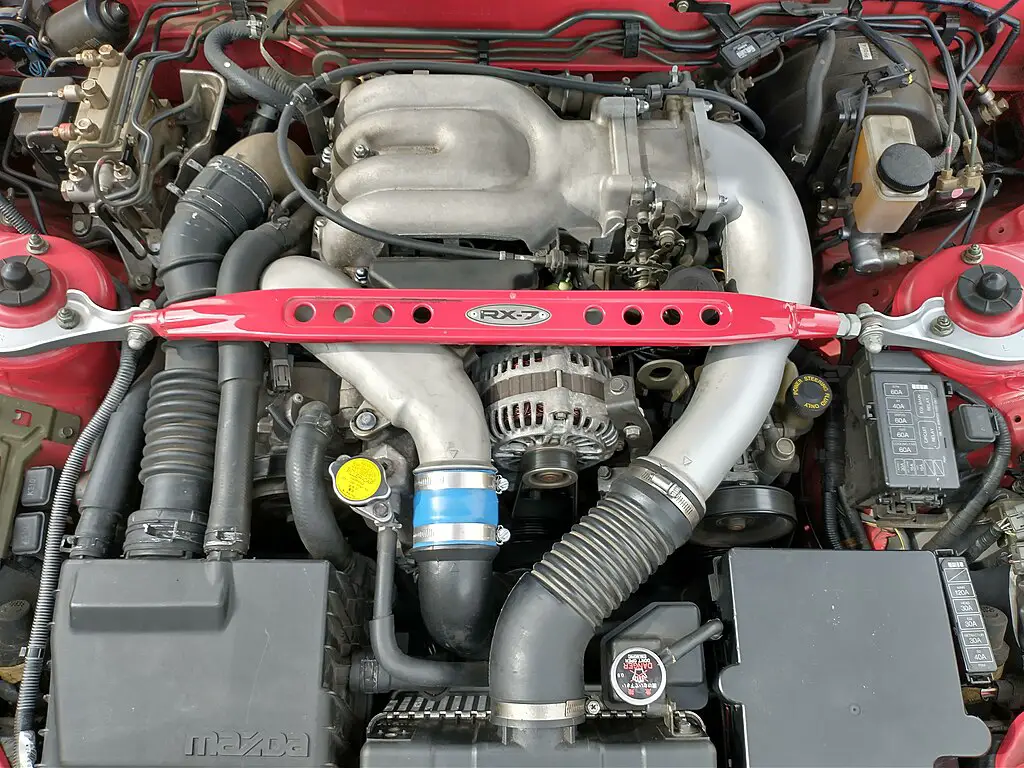
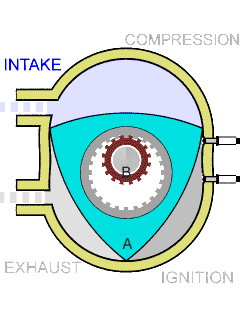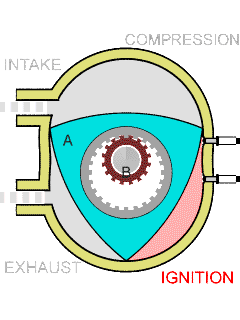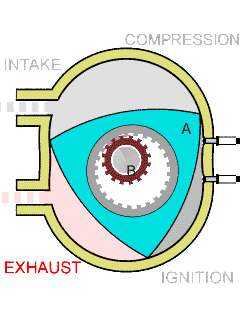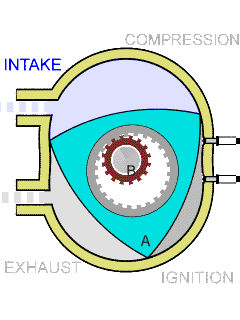
The RX-7 ran a rotary engine, also known as a Wankel engine, which was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel in the 1950s. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines that use pistons and cylinders to convert fuel into energy, rotary engines have a triangular-shaped rotor that spins within an oval-shaped housing. This design allowed for more compact and lightweight engines with higher power output.
With its sleek design and powerful rotary engine, the Mazda RX-7 quickly gained popularity among sports car enthusiasts. It even earned the title of Motor Trend’s Import Car of the Year in 1986. The success of the RX-7 prompted Mazda to continue improving and updating the model over.
1978 Mazda RX7 Taisyo, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
First Generation (SA/FB): 1978–1985
The first-generation RX-7, introduced in 1978, featured the 12A rotary engine. Known as the SA (later FB), this model quickly gained popularity for its agile handling and sleek design. Mazda’s commitment to innovation and performance was evident in this lightweight, affordable sports car.
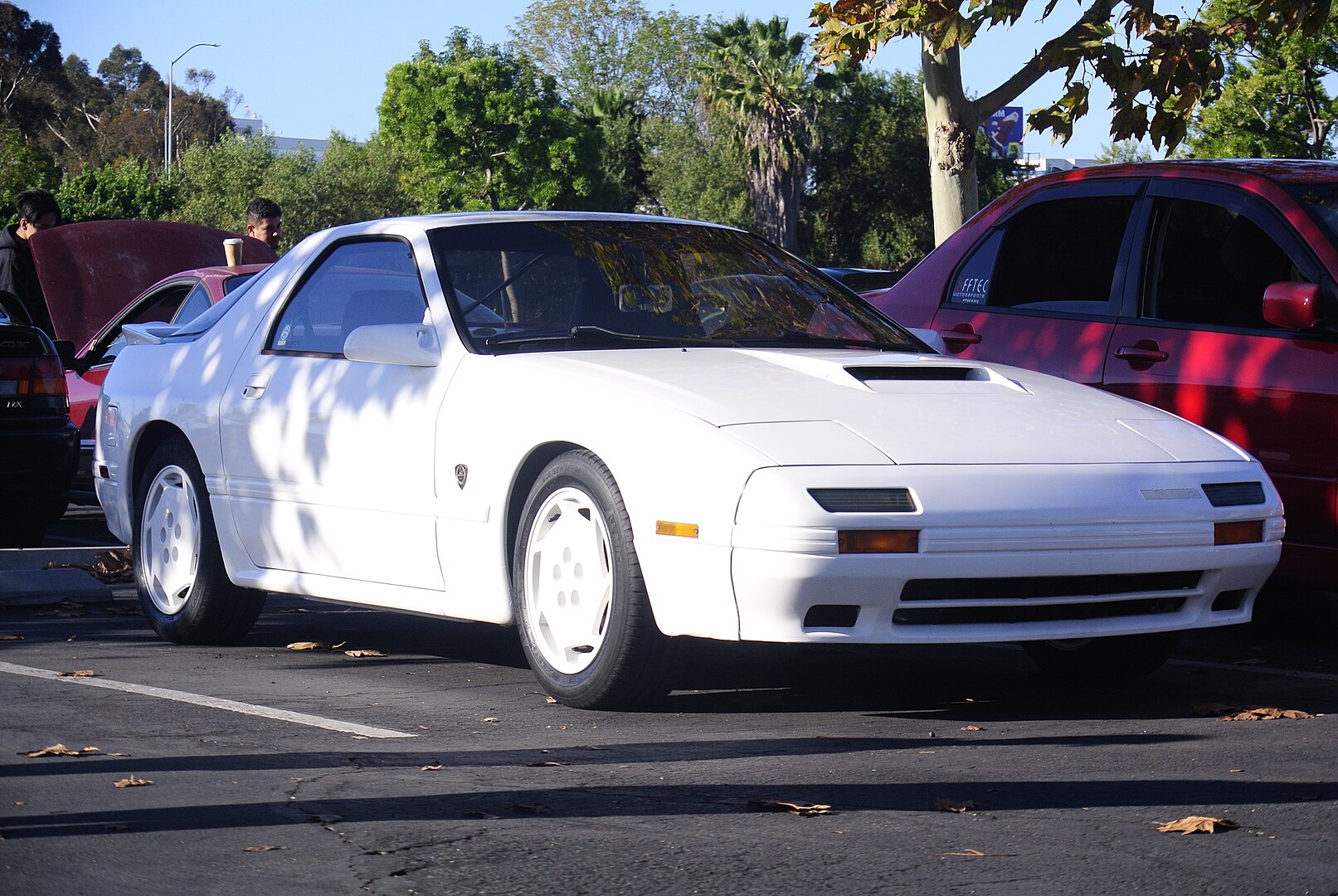

1988 Mazda RX7 10th Anniversary Edition
Second Generation (FC): 1986–1991
In 1986, the second-generation RX-7 (FC) hit the market, featuring improved aerodynamics, suspension, and a more refined interior. The introduction of the turbocharged 13B rotary engine offered even greater performance, making the FC RX-7 a favorite among driving enthusiasts.
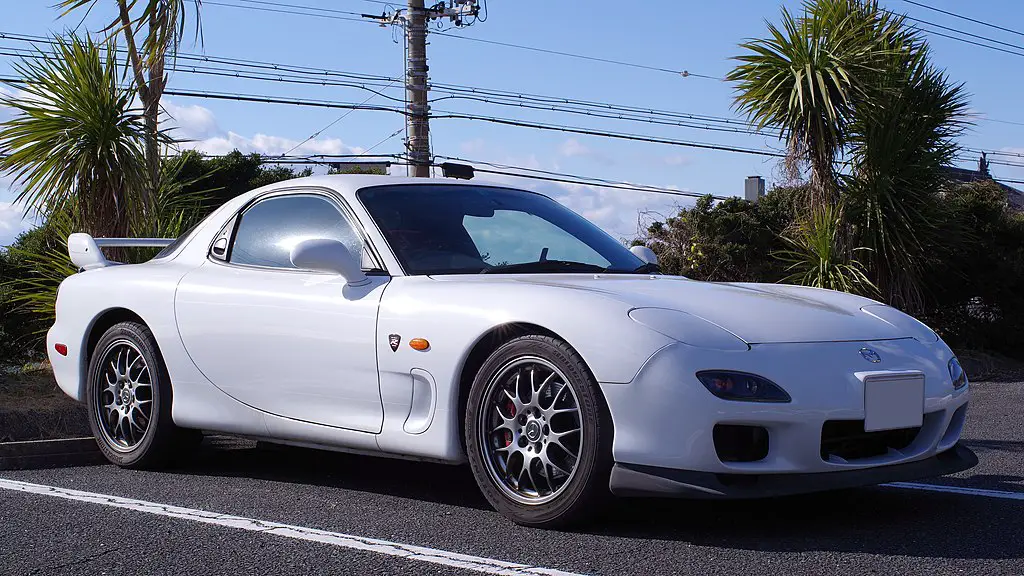
2002 Mazda RX7 ?????, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Third Generation (FD): 1992–2002
The third-generation RX-7 (FD) is perhaps the most beloved version of the car. Launched in 1992, it featured a twin-turbocharged 13B-REW rotary engine, producing up to 276 horsepower. Its lightweight design and near-perfect weight distribution made it one of the best-handling cars of its time. Despite its acclaim, the FD faced challenges such as stricter emissions regulations and declining sales, leading to its discontinuation in 2002.
The Rotary Engine: A Unique Marvel
The rotary engine, particularly showcased by the Mazda RX-7, is distinguished by several key features that enhance its efficiency and performance. It contains significantly fewer moving parts—typically 30 to 50 less than traditional piston engines—due to its design that relies on two or three rotors rather than pistons, rods, and valves. This simplicity not only streamlines manufacturing but also contributes to a lighter overall structure.
Additionally, the rotary engine’s compact design optimizes space, improving weight distribution and handling dynamics. Its operational smoothness is noteworthy as well, with minimal vibrations and noise thanks to the absence of reciprocating parts. The engine’s ability to achieve high RPMs, nearing 10,000, further underscores its performance capabilities. At the core of this innovative technology, developed by German engineer Felix Wankel, is a rotor that spins within an oval housing, delivering a powerful yet lightweight alternative to conventional engines.
Advantages of the Rotary Engine
- Fewer moving parts: A rotary engine consists of 30–50 fewer moving parts than a conventional piston engine due to the absence of pistons, connecting rods, valves, and a crankshaft. Instead, it utilises two or three rotors along with an output shaft.
- Space-saving design: The design of the rotary engine is more compact compared to piston engines, eliminating the need for cylinders.
- Quieter and smoother operation: The absence of reciprocating parts leads to reduced vibration and noise, resulting in a quieter and smoother driving experience.
- Higher speeds: With less rotating mass and no valves, the rotary engine can rev more freely and achieve higher speeds, reaching up to 10,000 rpm.
- Unique delivery system: The rotary engine executes key operations, including intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust, within separate housing sections, allowing for efficient performance.
Advantages of the Rotary Engine
- Compact and Lightweight: Its simple design results in a compact and lightweight engine.
- Fewer Moving Parts: The rotary engine has fewer moving parts compared to traditional engines, leading to less mechanical wear and tear.
- High Power-to-Weight Ratio: Its design allows for a higher power output relative to its size.
Challenges of the Rotary Engine
- Apex Seal Wear: One of the primary issues with rotary engines is the wear of apex seals, which can lead to decreased performance and reliability.
- Fuel Efficiency: Rotary engines are generally less fuel-efficient than their piston counterparts.
- Emission Standards: Meeting modern emission standards has been a significant hurdle for rotary engines.
Legacy and Impact of the Mazda RX-7
The RX-7’s legacy extends far beyond its production years. It remains a symbol of Mazda’s engineering prowess and dedication to pushing the boundaries of automotive design. The rotary engine, while no longer used in mass-produced vehicles, continues to captivate enthusiasts and engineers alike.
Perhaps a new Mazda RX7?
Mazda RX7 recently announced a prototype for a two-rotor engine, hinting at the potential revival of the RX series. This new engine could be installed in a performance vehicle, as seen in the Iconic SP concept, where the rotary engine would work as a generator to juice up the battery rather than being mechanically connected to the wheels.
Prototype Features
- Two Longitudinally Mounted Rotary Engines: Designed for power generation with a larger power supply and low center of gravity proportions.
- Improved Vibration and Emissions: Enhanced displacement aims to improve both vibration and emissions.
Potential Applications
Mazda’s Chief Designer, Masashi Nakayama, mentioned that the Iconic SP concept was intentionally made bigger to create a splash at the Japan Mobility Show. Although larger than necessary, the car could potentially be shrunk to the size of a Miata, accommodating the two-rotor engine, electric motor, and battery pack.
Conclusion
The Mazda RX-7 and its rotary engine represent a unique chapter in automotive history. While the rotary engine faced significant challenges, its innovative design and performance capabilities left a lasting impact. With Mazda’s recent developments, the future of the rotary engine looks promising, potentially heralding a new era for this iconic technology.