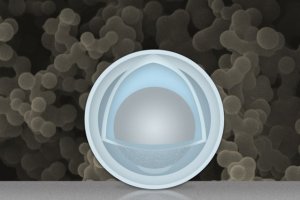
One big problem faced by electrodes in rechargeable batteries, as they go through repeated cycles of charging and discharging, is that they must expand and shrink during each cycle — sometimes doubling in volume, and then shrinking back. This can lead to repeated shedding and reformation of its “skin” layer that consumes lithium irreversibly, degrading the battery’s performance over time. Now researchers have found a novel way around that problem: creating an electrode made of nanoparticles with a solid shell, and a “yolk” inside that can change size again and again without affecting the shell.
SOURCE: Batteries News — ScienceDaily – Read entire story here.







