Finding a way to boost efficiency of CIGS solar cells
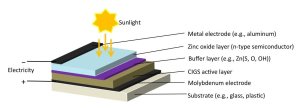
Researchers have revealed the structure of the buffer layer in a CIGS (copper-indium-gallium-selenide) solar cell at SPring8, the world’s largest third-generation synchrotron radiation facility. They found that the buffer layer was composed of two layers: an upper Zn(OH)2 layer and a lower Zn(S, O) layer. By removing the upper Zn(OH)2 layer, the solar conversion efficiency was doubled.